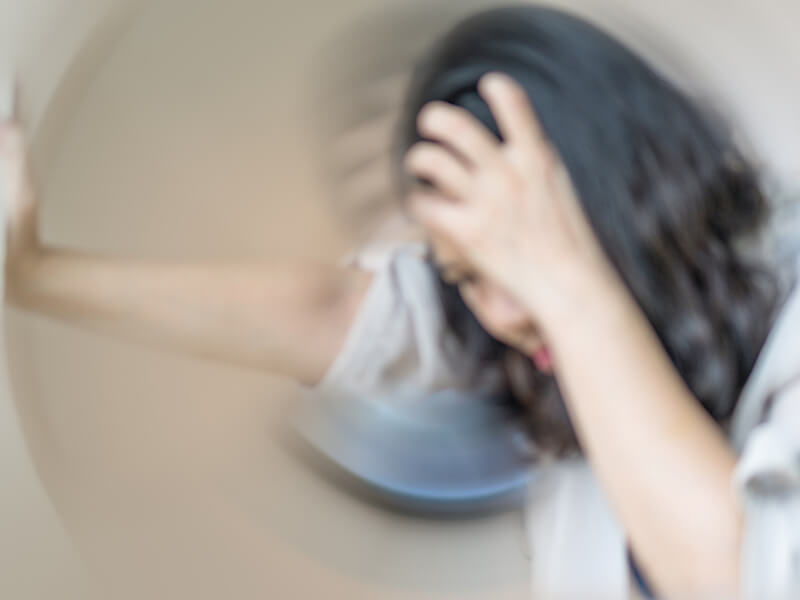
The cause of Meniere’s isn’t really understood. But the effects are difficult to underestimate. Some common symptoms of this disorder are dizziness, vertigo, ringing in the ears, and hearing loss. Experts aren’t really certain why, but for some reason, fluid can accumulate in the ears and this appears to be the underlying cause of Meniere’s disease.
So here’s the question: how can you treat something that doesn’t seem to have a discernible cause? It’s a complicated answer.
Exactly what is Meniere’s disease?
Meniere’s disease is a chronic disorder that impacts the inner ear. Symptoms of Meniere’s will get worse over time, for many people, because it’s a progressive disease. Here are some of those symptoms:
Unpredictable bouts of vertigo: Unfortunately, there’s no way to tell when these attacks of vertigo will strike or how long they could last.
Tinnitus: It’s fairly common for individuals with Meniere’s disease to have ringing in the ears or tinnitus, which can range from mild to severe.
Fullness in the ear: This manifests as a sensation of pressure in your ears and is medically called aural fullness.
Hearing loss: In the long run, Meniere’s disease can lead to a loss of hearing.
It’s critical that you get the proper diagnosis if you’re experiencing these symptoms. Symptoms of Meniere’s disease can come and go for many people. But over time, symptoms may become more regular and obvious.
Treatment for Menier’s disease
There is no known cure for Menier’s disease which is chronic and progressive. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t any way to treat it.
The following are a few of those treatments:
- Hearing aid: As Meniere’s disease progresses and your hearing loss grows worse, you may want to get a hearing aid. Typically, a hearing aid won’t necessarily slow the progress of your hearing loss. But it can help your mental health by keeping you socially active. Hearing aids can also help you manage the symptoms of tinnitus in a number of ways.
- Surgery: In some situations, surgery is utilized to address Meniere’s. However, these surgical techniques will typically only affect the vertigo part of symptoms. Other Meniere’s symptoms will continue.
- Medications: In some situations, your doctor will be able to prescribe anti-dizziness and anti-nausea medications. If those specific symptoms show up, this can be helpful. For example, medications created to help with motion sickness may help you feel less dizzy when an episode of vertigo occurs.
- Diuretic: A diuretic is another medication alternative that might be prescribed by your physician. The idea here is that the pressure in the inner ear can be minimized by reducing fluid retention. This is a long-term medication that you’d use rather than one to minimize severe symptoms.
- Steroid shots: Some symptoms of Meniere’s, especially vertigo, can be temporarily alleviated with injections of certain steroids.
- Positive pressure therapy: There’s a non-invasive method used when Meniere’s is especially difficult to manage. It’s known as positive pressure therapy. As a way to limit fluid buildup, the inner ear is subjected to positive pressure. While positive pressure therapy is promising, the long-term advantages of this approach have not been borne out by peer-reviewed research.
- Rehabilitation: There are rehabilitation and physical therapy strategies that can help you maintain balance when Meniere’s disease is flaring up. This approach may be a useful strategy if you’re experiencing frequent dizziness or vertigo.
The key is finding the treatment that’s best for you
You should get checked out if think you might have Meniere’s disease. The advancement of Meniere’s disease might be slowed by these treatments. More frequently, however, they reduce the effect that Meniere’s will have on your daily life.